Understanding user behavior and preferences is essential for creating effective and user-friendly designs. While usability testing is a critical part of user research, there are many other methods that can provide valuable insights. Here are 15 user research methods beyond usability testing that can help you gather comprehensive data about your users.
1. Interviews
Description:
Interviews involve direct conversations with users to gather in-depth insights into their experiences, needs, and motivations. They can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
Benefits:
- Provides detailed qualitative data.
- Allows for follow-up questions and probing deeper into responses.
- Helps in understanding the user’s perspective and experiences.
Best Practices:
- Prepare a list of open-ended questions.
- Build rapport with the interviewee to make them comfortable.
- Record the sessions (with permission) for accurate data analysis.
2. Surveys and Questionnaires
Description:
Surveys and questionnaires are effective for collecting quantitative data from a large number of users. They can cover a wide range of topics and provide insights into user preferences and behaviors.
Benefits:
- Can reach a large audience.
- Provides statistical data that can be easily analyzed.
- Cost-effective and easy to distribute.
Best Practices:
- Keep questions clear and concise.
- Use a mix of question types (e.g., multiple-choice, Likert scale).
- Pre-test your survey to identify potential issues.
3. Focus Groups
Description:
Focus groups involve moderated discussions with a group of users to explore their attitudes, feelings, and perceptions about a product or service. This method is useful for generating ideas and understanding user needs.
Benefits:
- Encourages interaction and discussion among participants.
- Provides diverse perspectives.
- Can generate new ideas and insights.
Best Practices:
- Select a diverse group of participants.
- Use a skilled moderator to guide the discussion.
- Ensure a comfortable and neutral environment for participants.
4. Field Studies
Description:
Field studies involve observing users in their natural environment. This method provides context-rich insights into how users interact with products in real-world settings.
Benefits:
- Captures authentic user behavior.
- Provides context for user actions and decisions.
- Helps identify unarticulated needs and pain points.
Best Practices:
- Spend sufficient time observing users.
- Take detailed notes and photographs (with permission).
- Avoid interfering with the user’s natural behavior.
5. Card Sorting
Description:
Card sorting helps in organizing information in a way that makes sense to users. Participants organize topics into categories, which helps in creating an intuitive information architecture for websites and applications.
Benefits:
- Provides insights into how users categorize information.
- Helps in designing intuitive navigation structures.
- Can be conducted in-person or online.
Best Practices:
- Use clear and descriptive card labels.
- Allow users to create their own categories.
- Analyze results to identify common patterns.
6. Tree Testing
Description:
Tree testing evaluates the findability of topics in a website’s hierarchy. Users are asked to find specific items in a simplified text version of the site’s structure to identify navigation issues.
Benefits:
- Identifies areas where users struggle to find information.
- Helps improve website navigation.
- Provides quantitative data on success rates and time taken.
Best Practices:
- Test with a representative sample of users.
- Use clear and realistic tasks.
- Analyze results to pinpoint specific problem areas.
7. A/B Testing
Description:
A/B testing compares two versions of a webpage or app to see which one performs better. It helps in making data-driven design decisions.
Benefits:
- Provides direct evidence of what works better.
- Can lead to significant improvements in user experience.
- Reduces the risk of implementing ineffective changes.
Best Practices:
- Test one variable at a time to isolate effects.
- Ensure a large enough sample size for statistical significance.
- Monitor results and iterate based on findings.
8. Heatmaps
Description:
Heatmaps visually represent where users click, scroll, and move on a webpage. This method highlights areas of interest and potential issues in the design.
Benefits:
- Provides visual data on user interactions.
- Identifies hotspots and areas of neglect.
- Easy to understand and interpret.
Best Practices:
- Use heatmaps alongside other methods for a complete picture.
- Compare heatmaps before and after design changes.
- Focus on key areas that align with user goals.
9. Eye Tracking
Description:
Eye tracking technology tracks where users look on a screen. It provides insights into visual attention and helps in understanding user behavior and preferences.
Benefits:
- Reveals what captures user attention.
- Helps in optimizing visual hierarchy and layout.
- Provides objective data on visual behavior.
Best Practices:
- Ensure participants are comfortable with the equipment.
- Use tasks that reflect real user goals.
- Combine with other data for comprehensive insights.
10. Diary Studies
Description:
Diary studies involve users recording their experiences and interactions with a product over time. This method provides long-term insights into user behavior and satisfaction.
Benefits:
- Captures data over an extended period.
- Provides context for user behavior and decisions.
- Helps identify trends and patterns.
Best Practices:
- Provide clear instructions and prompts.
- Check-in regularly with participants.
- Analyze entries for recurring themes and insights.
11. Ethnographic Research
Description:
Ethnographic research involves immersive observation of users in their natural environment. It provides deep insights into user behaviors, cultures, and contexts.
Benefits:
- Offers a holistic view of user experiences.
- Captures contextual factors that influence behavior.
- Identifies unarticulated needs and pain points.
Best Practices:
- Spend significant time in the field.
- Build rapport with participants.
- Use multiple data collection methods (e.g., observation, interviews).
12. Contextual Inquiry
Description:
Contextual inquiry is a blend of interviews and observation conducted in the user’s environment. It helps in understanding the context of use and identifying pain points and opportunities.
Benefits:
- Provides detailed insights into user workflows and contexts.
- Identifies real-world challenges and opportunities.
- Encourages collaboration between researchers and participants.
Best Practices:
- Conduct sessions in the user’s environment.
- Use open-ended questions and observation.
- Document findings thoroughly.
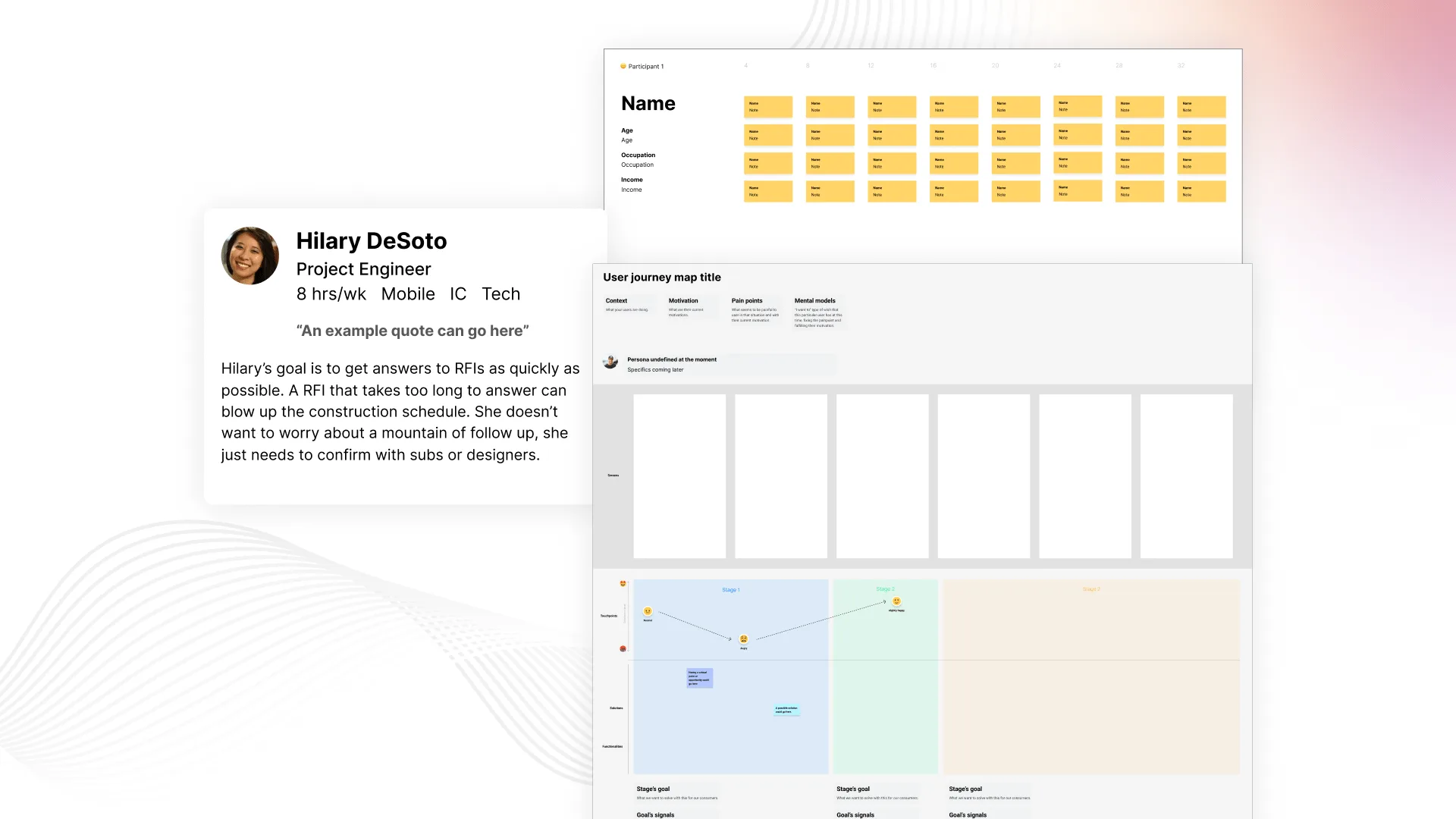
13. Personas
Description:
Personas are fictional characters created based on user research to represent different user types. They help in keeping the user in mind throughout the design process.
Benefits:
- Humanizes user data.
- Helps align the team on user needs and goals.
- Guides design decisions and prioritization.
Best Practices:
- Base personas on real user data.
- Include demographic, psychographic, and behavioral details.
- Use personas throughout the project lifecycle.
14. Journey Mapping
Description:
Journey mapping visualizes the user’s experience with a product or service over time. It identifies touchpoints, pain points, and opportunities for improvement.
Benefits:
- Provides a holistic view of the user experience.
- Identifies critical moments in the user journey.
- Helps prioritize areas for improvement.
Best Practices:
- Involve stakeholders in the mapping process.
- Use data from multiple sources (e.g., interviews, analytics).
- Update maps as new data becomes available.
15. Competitor Analysis
Description:
Competitor analysis involves studying competitors’ products to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. It helps in understanding the market and positioning your product effectively.
Benefits:
- Identifies industry trends and standards.
- Uncovers competitor strengths and weaknesses.
- Informs strategic decisions and differentiation.
Best Practices:
- Analyze a range of competitors.
- Focus on both direct and indirect competitors.
- Regularly update your analysis.
Conclusion
Using a variety of user research methods beyond usability testing can provide a comprehensive understanding of your users. At UIUX Studio, we employ these methods to ensure that our designs are user-centered and effective. By combining qualitative and quantitative data, we gain insights that drive innovation and improve user experiences.
By employing these diverse research methods, you can gain a richer understanding of your users and create more effective, user-centered designs. At UIUX Studio, we are committed to utilizing the best research practices to deliver exceptional user experiences.